#include <math.h>#include "wcsconfig.h"Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | WCSTRIG_TOL 1e-10 |
| Domain tolerance for asin() and acos() functions. More... | |
Functions | |
| double | cosd (double angle) |
| Cosine of an angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | sind (double angle) |
| Sine of an angle in degrees. More... | |
| void | sincosd (double angle, double *sin, double *cos) |
| Sine and cosine of an angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | tand (double angle) |
| Tangent of an angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | acosd (double x) |
| Inverse cosine, returning angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | asind (double y) |
| Inverse sine, returning angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | atand (double s) |
| Inverse tangent, returning angle in degrees. More... | |
| double | atan2d (double y, double x) |
Polar angle of 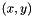 , in degrees. More... , in degrees. More... | |
Detailed Description
When dealing with celestial coordinate systems and spherical projections (some moreso than others) it is often desirable to use an angular measure that provides an exact representation of the latitude of the north or south pole. The WCSLIB routines use the following trigonometric functions that take or return angles in degrees:
These "trigd" routines are expected to handle angles that are a multiple of 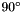 returning an exact result. Some C implementations provide these as part of a system library and in such cases it may (or may not!) be preferable to use them. WCSLIB provides wrappers on the standard trig functions based on radian measure, adding tests for multiples of
returning an exact result. Some C implementations provide these as part of a system library and in such cases it may (or may not!) be preferable to use them. WCSLIB provides wrappers on the standard trig functions based on radian measure, adding tests for multiples of 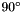 .
.
However, wcstrig.h also provides the choice of using preprocessor macro implementations of the trigd functions that don't test for multiples of 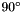 (compile with -DWCSTRIG_MACRO). These are typically 20% faster but may lead to problems near the poles.
(compile with -DWCSTRIG_MACRO). These are typically 20% faster but may lead to problems near the poles.
Macro Definition Documentation
| #define WCSTRIG_TOL 1e-10 |
Domain tolerance for the asin() and acos() functions to allow for floating point rounding errors.
If 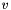 lies in the range
lies in the range 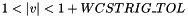 then it will be treated as
then it will be treated as 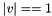 .
.
Function Documentation
| double cosd | ( | double | angle) |
cosd() returns the cosine of an angle given in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] angle [deg].
- Returns
- Cosine of the angle.
| double sind | ( | double | angle) |
sind() returns the sine of an angle given in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] angle [deg].
- Returns
- Sine of the angle.
| void sincosd | ( | double | angle, |
| double * | sin, | ||
| double * | cos | ||
| ) |
sincosd() returns the sine and cosine of an angle given in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] angle [deg]. [out] sin Sine of the angle. [out] cos Cosine of the angle.
- Returns
| double tand | ( | double | angle) |
tand() returns the tangent of an angle given in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] angle [deg].
- Returns
- Tangent of the angle.
| double acosd | ( | double | x) |
acosd() returns the inverse cosine in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] x in the range [-1,1].
- Returns
- Inverse cosine of x [deg].
| double asind | ( | double | y) |
asind() returns the inverse sine in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] y in the range [-1,1].
- Returns
- Inverse sine of y [deg].
| double atand | ( | double | s) |
atand() returns the inverse tangent in degrees.
- Parameters
-
[in] s
- Returns
- Inverse tangent of s [deg].
| double atan2d | ( | double | y, |
| double | x | ||
| ) |
atan2d() returns the polar angle, 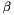 , in degrees, of polar coordinates
, in degrees, of polar coordinates 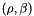 corresponding Cartesian coordinates
corresponding Cartesian coordinates 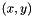 . It is equivalent to the
. It is equivalent to the 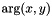 function of WCS Paper II, though with transposed arguments.
function of WCS Paper II, though with transposed arguments.
- Parameters
-
[in] y Cartesian 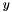 -coordinate.
-coordinate. [in] x Cartesian 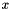 -coordinate.
-coordinate.
- Returns
- Polar angle of
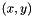 [deg].
[deg].
 1.8.4
1.8.4